Enhancing UX: Custom Wheel Navigation for Swiper Sliders with React Hooks
Enhancing User Experience with Custom Wheel Navigation for Swiper Sliders
Introduction to Wheel Event Handling
In modern web applications, intuitive navigation methods significantly impact user experience. While touch gestures dominate mobile interfaces, mouse wheel interactions remain a cornerstone of desktop navigation. Recognizing this, we set out to create a seamless scrolling experience for our Immersiview project by implementing custom wheel event handling for Swiper sliders.
The Challenge: Code Duplication and Maintenance
Our project featured two key components: ImageSlider and VideoSlider, both built using the Swiper library. Initially, each component contained identical wheel event handling logic:
typescript// Wheel event handling logic in ImageSlider.tsx useEffect(() => { const handleWheel = (e: WheelEvent) => { e.preventDefault(); if (swiperInstance) { if (e.deltaY > 0) { swiperInstance.slideNext(); } else { swiperInstance.slidePrev(); } } }; window.addEventListener("wheel", handleWheel, { passive: false }); return () => window.removeEventListener("wheel", handleWheel); }, [swiperInstance]); // Identical logic was also present in VideoSlider.tsx
This approach introduced several issues:
- Code duplication: The same logic was maintained in multiple places
- Maintenance overhead: Any future changes would require updates in multiple components
- Inconsistency risk: Slight modifications could inadvertently create divergent behavior
Implementing a Reusable Solution
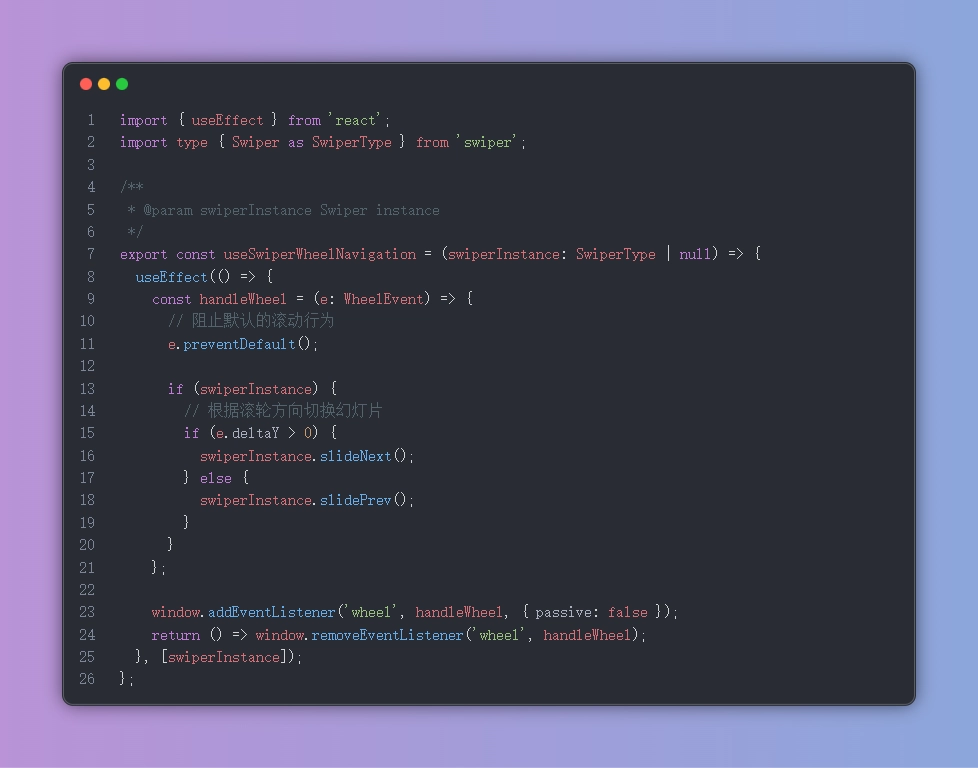
To address these challenges, we extracted the wheel event handling logic into a custom React Hook. This approach follows the Don't Repeat Yourself (DRY) principle and promotes code reusability across components.
typescript// hooks/useSwiperWheelNavigation.ts import { useEffect } from 'react'; import type { Swiper as SwiperType } from 'swiper'; /** * Custom Hook to enable wheel navigation for Swiper instances * @param swiperInstance The Swiper instance to attach wheel navigation to */ export const useSwiperWheelNavigation = (swiperInstance: SwiperType | null) => { useEffect(() => { const handleWheel = (e: WheelEvent) => { // Prevent default browser scrolling behavior e.preventDefault(); if (swiperInstance) { // Navigate to next or previous slide based on wheel direction if (e.deltaY > 0) { swiperInstance.slideNext(); } else { swiperInstance.slidePrev(); } } }; window.addEventListener('wheel', handleWheel, { passive: false }); return () => window.removeEventListener('wheel', handleWheel); }, [swiperInstance]); };
Integration and Benefits
With the hook in place, integrating wheel navigation into our slider components became remarkably straightforward:
tsx// In ImageSlider.tsx import { useSwiperWheelNavigation } from "../../hooks/useSwiperWheelNavigation"; // ... useSwiperWheelNavigation(swiperInstance); // ... // Similarly in VideoSlider.tsx import { useSwiperWheelNavigation } from "../../hooks/useSwiperWheelNavigation"; // ... useSwiperWheelNavigation(swiperInstance); // ...
This implementation offers several significant advantages:
- Code Reusability: The same navigation logic can be easily applied to any Swiper-based component
- Improved Maintainability: Updates to the wheel navigation behavior only need to be made in one location
- Consistent User Experience: All sliders respond to wheel events in the same intuitive manner
- Cleaner Component Code: Slider components focus on their core functionality rather than event handling logic
Technical Implementation Details
Preventing Default Browser Behavior
A critical aspect of our implementation is calling e.preventDefault() within the wheel event handler. This prevents the browser from interpreting wheel events as page scrolling, ensuring that all wheel interactions are dedicated to slider navigation.
The Passive Option
We explicitly set { passive: false } when adding the event listener. This is necessary because, in modern browsers, wheel events are often passive by default (meaning their default behavior cannot be prevented). By setting passive: false, we ensure that e.preventDefault() works as expected across different browsers.
Memory Management
The hook properly cleans up the event listener when the component unmounts or when the swiperInstance changes. This prevents memory leaks and ensures optimal performance throughout the application lifecycle.
Best Practices Applied
This implementation demonstrates several important software engineering best practices:
- Abstraction: Complex logic is encapsulated within a reusable hook
- Separation of Concerns: Event handling is separated from component rendering logic
- Type Safety: The use of TypeScript ensures type safety throughout the implementation
- Performance Optimization: Efficient event handling and proper cleanup prevent performance issues
Conclusion
By extracting wheel event handling into a custom React Hook, we've significantly improved our codebase's maintainability while enhancing the user experience with intuitive navigation controls. This approach demonstrates how thoughtful architecture decisions can simultaneously solve technical challenges and improve product quality.
The useSwiperWheelNavigation hook is a perfect example of how React's compositional model enables developers to create reusable, maintainable code without sacrificing functionality or performance. For any project utilizing Swiper components, implementing similar navigation patterns can provide users with a more natural and engaging browsing experience.